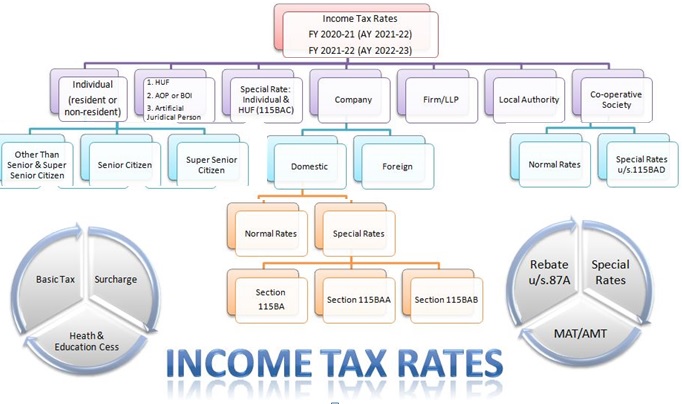
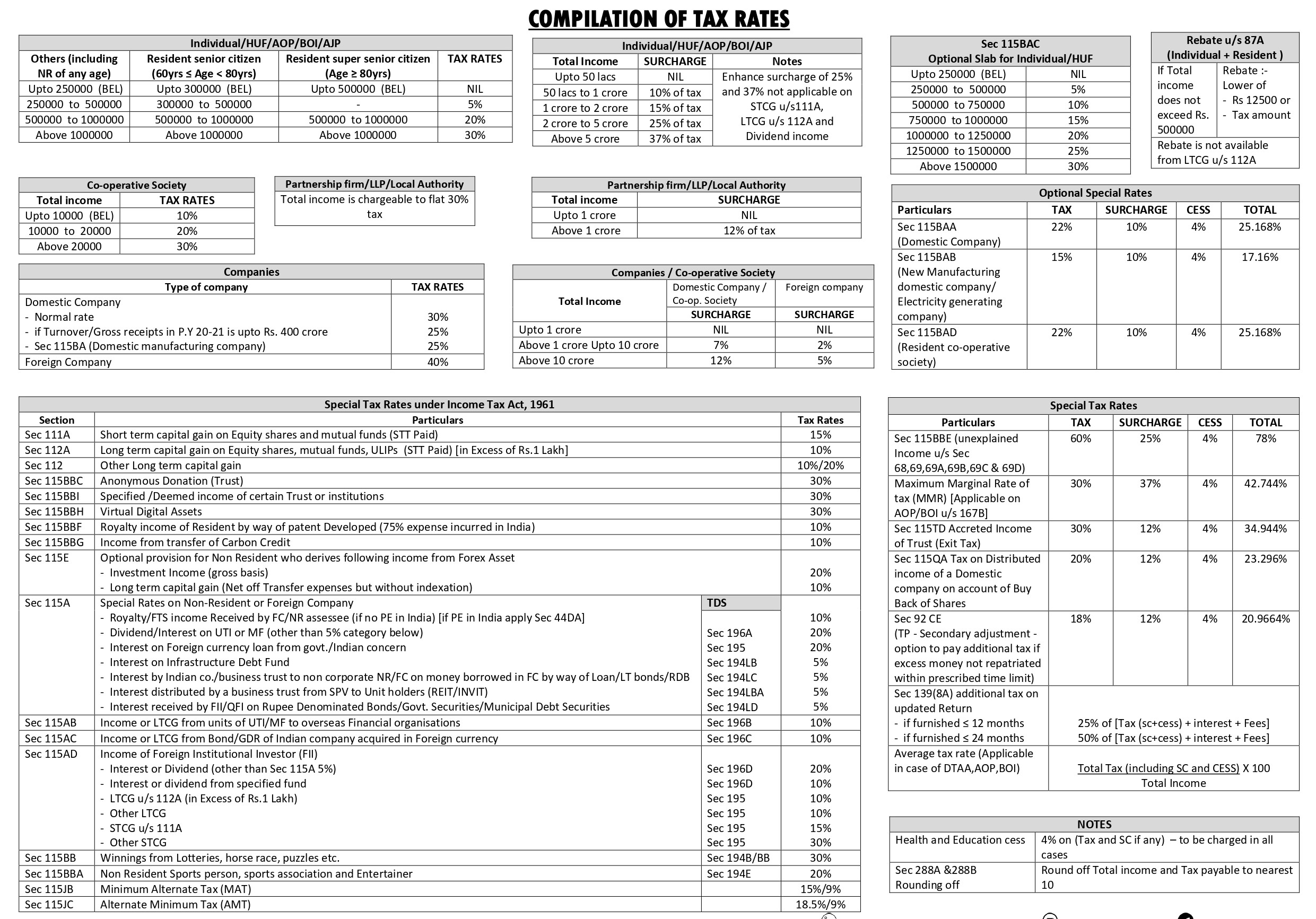
Complete understanding LLP Compliances
COMPLETE UNDERSTANDING LLP COMPLIANCES
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), governed by the LLP Act 2008 came into force on 31/03/2009. The main objective behind such type of partnership was to introduce a type of business form which is a perfect combination of the operational easiness and flexibility of a partnership firm along with the limited liability of its partners which was earlier a limitation of partnership firm formed under Indian Partnership Act, 1932.
- In an LLP the formation of a partner is quite unique in the sense that there are two designated partners who give their name and consent to become the partner of the concerned LLP, at the time of its formation. Also, none of the partners can be held responsible for any misconduct or negligence leading to imposition of any penalty or causing loss to the LLP. Just like the directors in a company, the designated partners have the right as well as the duty to manage internal and external business affairs, specifically assigned, in accordance with the LLP Agreement.
- The partners are responsible for annual compliance of their business in terms of proper maintenance of books of accounts, filing of ITR and filing return with MCA, within the due date prescribed.
BENEFITS OF LLP
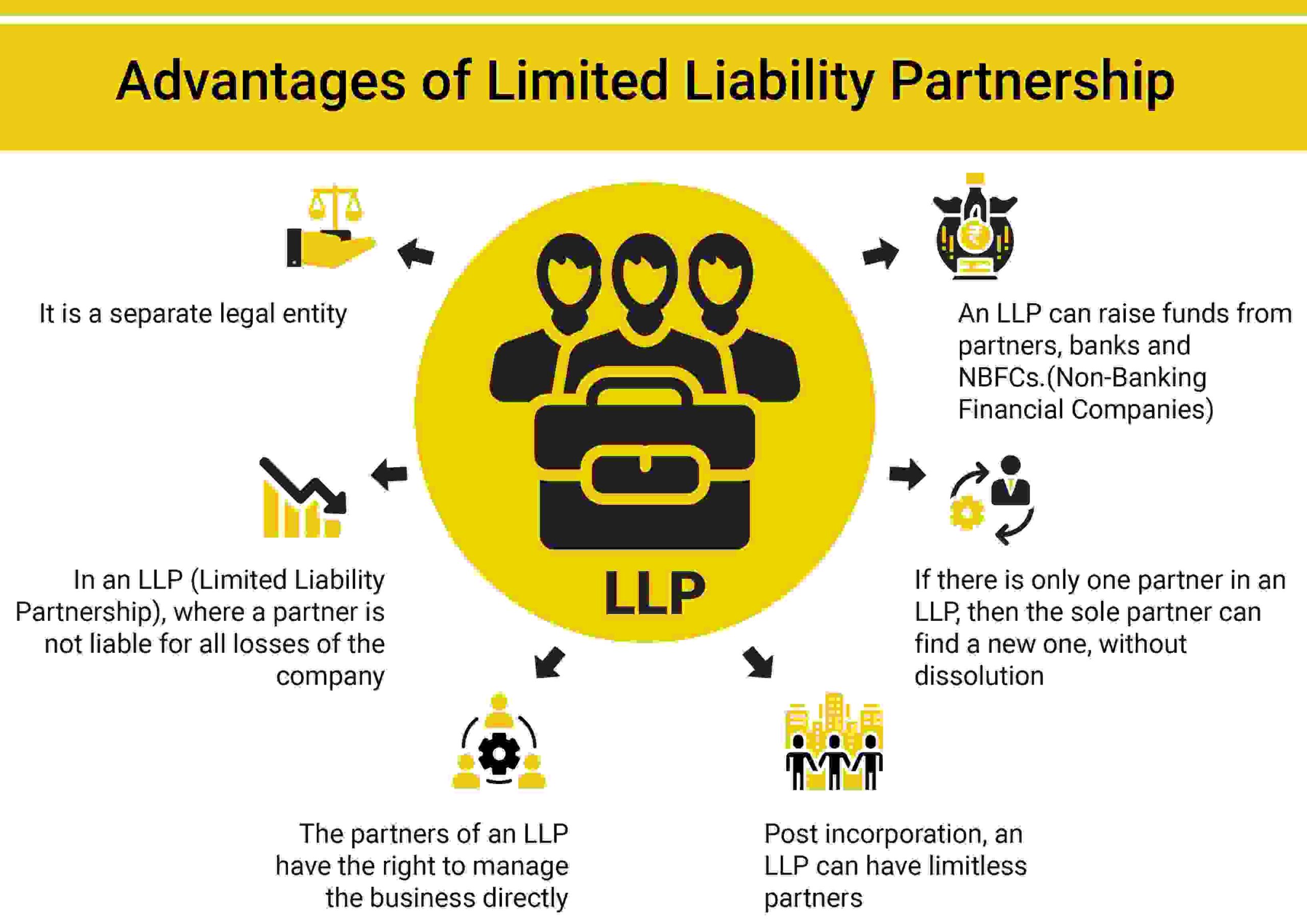
- PARTNERS ARE THE AGENT OF LLP – One of the main features is that, all the partners of the LLP, shall be agents of such LLP i.e., any act of partners will make the LLP accountable for the same but any partner’s act cannot bind another partner. Thus, partners of the LLP cannot be held liable and responsible for the misconduct or negligence of another partner.
- CONTROL OVER MANAGEMENT – Partners of LLPs have full control over the business affairs and can freely sort out their management problems.
- LIMITED LIABILITY – The partners of the LLP are having limited liabilities, which means that in case the assets of the LLP become insufficient to pay any liability, then the partners are liable only to the extent of their contribution and thus cannot be asked to pay from their personal assets.
- LACK OF REQUISITE MEMBERS – Where the total number of partners reduces to 1, due to any disability or death of any partner, the remaining partner can still continue the business operations, provided a new partner joins the LLP within 6 months from the date, the total partners fall below 2.
- NUMBER OF PARTNER – Unlike a partnership firm, and LLP shall have a minimum of 2 partners who will be the designated partners. There is no ceiling on the maximum partners.
- SEPARATE LEGAL ENTITY – LLP, unlike partnership firm, is a body corporate having separate legal entities from its partners. Thus, they can hold assets in their own name and can also sue or be sued by any other person.
- COST INVOLVED – The cost of formation of LLP is quite lesser than other forms of business and also the compliance cost is also very less.
- PERPETUAL SUCCESSION – LLP, just like a company is having perpetual succession, which means that the retirement, death, and leaving of firm by any partner or group of partners, will not affect the existence of the LLP.
- NO MINIMUM CAPITAL REQUIRED – There is no restriction on minimum capital contribution for the formation of the LLP.
- NO MUTUAL AGENCY – The partners of the LLP cannot be held liable and responsible for the misconduct or negligence of another
- EASE OF FORMATION – LLP is much simpler and less time consuming in terms of formation.
- EASE OF COMPLIANCE AND RESTRICTIONS – There are very less restrictions and compliances required to be fulfilled by the LLP.
- EASE IN RAISING FUNDS – An LLP can get access to funds from Banks and NBFCs, quite easily.
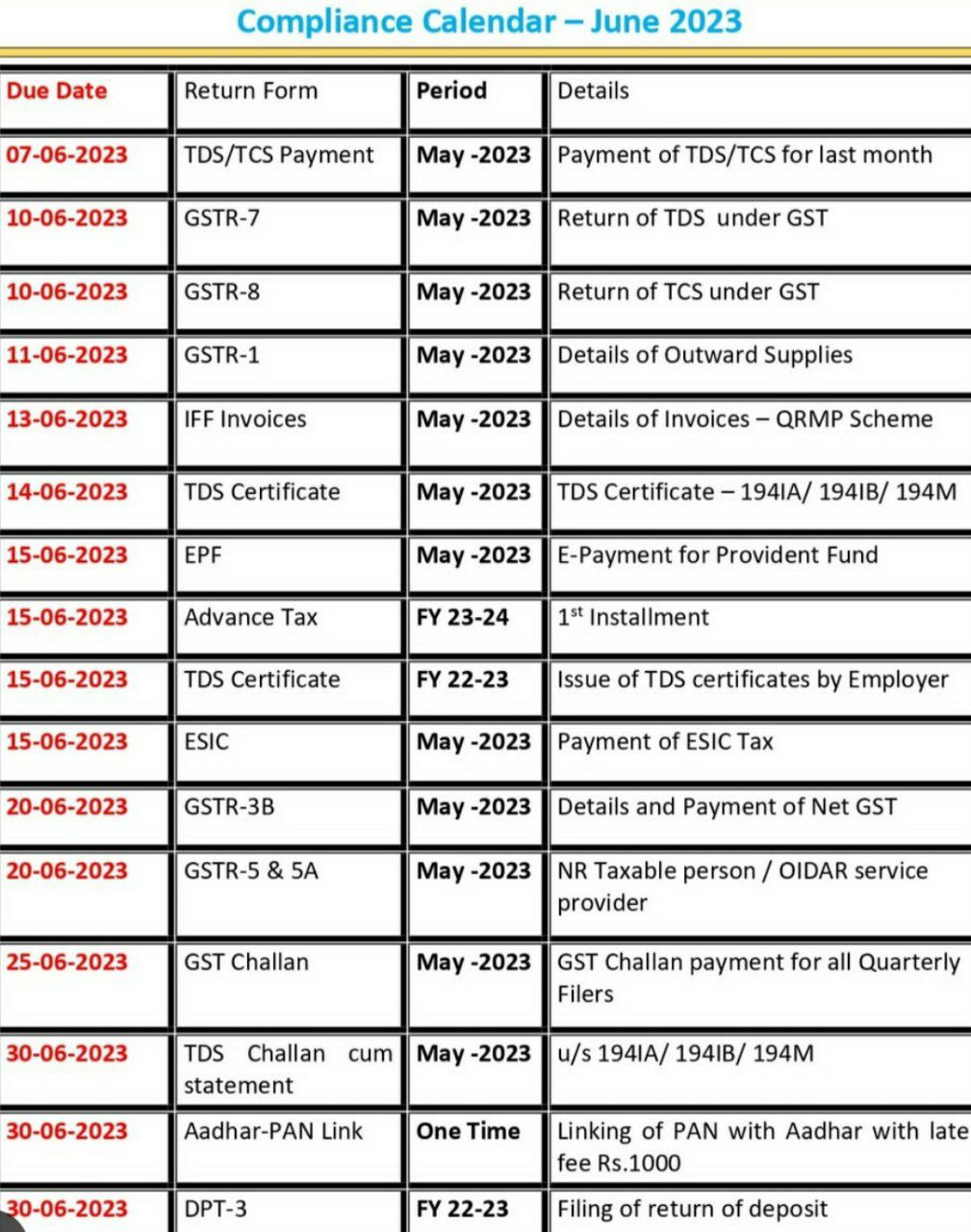
STATUTORY COMPLIANCES
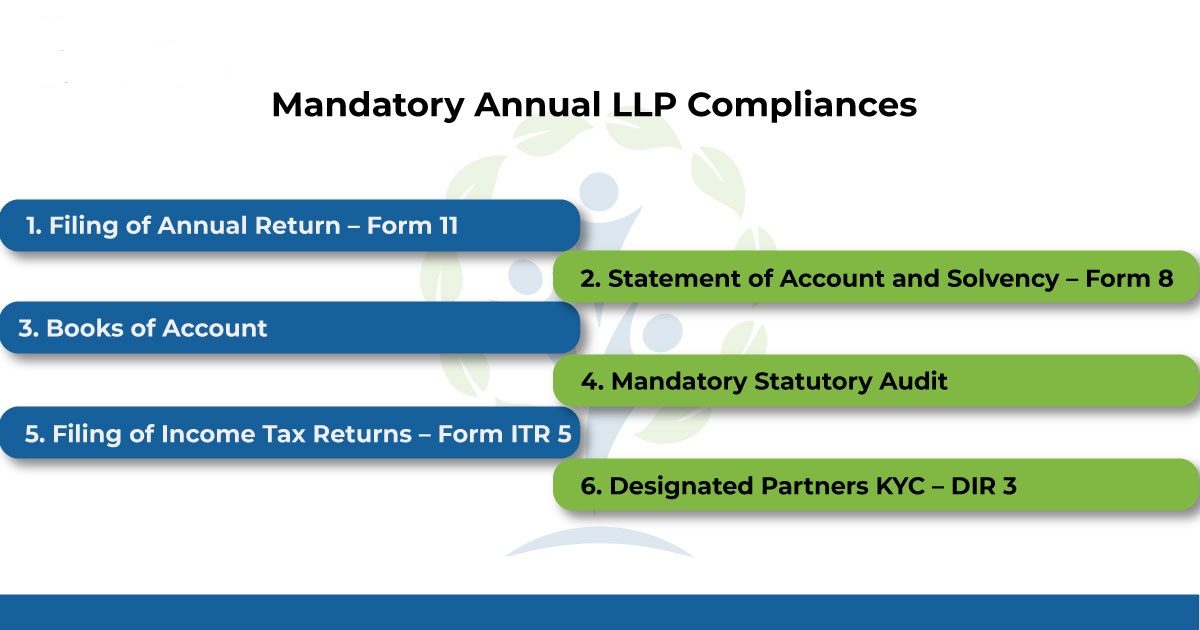
All LLPs are required to get compulsory registration under MCA in India and such LLP is required to file their statement of Accounts and Annual Returns of each financial year, within the prescribed due dates. Generally, there are three compliances commonly required to be fulfilled by a LLP, namely –
- Filing of annual return for each of the financial year.
- Time filing of Income Tax Returns, on and before the prescribed due date.
- Properly prepared books of accounts, prescribed by MCA.
ANNUAL RETURN
- Annual Return describes the details of LLP’s partners and the same is filed in Form 11. It also states about any changes made in the working of management or its personnel during the respective financial year. Annual return be filed in Form 11, within 60 days from the closure of the respective financial year, with the Registrar of Companies. Thus, the due date is 30th May, coming after the end of the respective financial year.
- Annual return in Form 11 applies to LLPs formed/registered on and before 30th September 2017. Those registered after 30th September 2017 can file their return in 2019.
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
- Every business, whether a company or an LLP, is required to maintain proper books of accounts, following the principles of the Double Entry System. Along with statement of accounts, a Statement of Solvency (Accounts) is also required to be prepared and submitted, every financial year. For this, Form 8 is required to be filed by the LLP Registrar of Companies on or before 30th October every year.
- Statement of accounts in Form 8 applies to LLPs formed/registered on and before 30th September 2017. Those registered after 30th September 2017 can file their statements in 2019.
INCOME TAX
- As per Income Tax Act, 1961, every LLP having annual turnover exceeding Rs.40 lakhs or capital contribution exceeding Rs.25 Lakhs, are required to get their books of account audited by a Practicing Chartered Accountant. In respect of ITR filing, the due date is 30th September coming after the end of the respective financial year, for LLP requiring audit of their books of accounts. Where audit is not required, the said due date is 31st July coming after the end of the respective financial year.
- Apart from above two due dates, LLPs undertaking international transactions and are required to file Form 3CEB, shall file their ITR, on and before 30th November coming after the end of respective financial year. MCA has prescribed Form ITR5 for LLPs ITR filing. The said form needs to be authorized by the partners using their respective digital signature. The whole process is initiated online on the Income Tax portal and the payment of requisite tax be made using the E-payment modes/options available on the website.
SUMMARIZED DUE DATES
| PARTICULARS | DUE DATE | |
| ANNUAL RETURN | FORM 11 FOR ANNUAL RETURN | 30th MAY, AFTER THE END OF FY |
| FORM 8 FOR FINANCIAL ACCOUNTS | 30th OCTOBER, AFTER THE END OF FY | |
| INCOME TAX RETURN | AUDIT NOT REQUIRED | 31st JULY, AFTER THE END OF FY |
| AUDIT REQUIRED | 30th SEPTEMBER, AFTER THE END OF FY | |
| REQUIRED TO FILE FORM 3CEB | 30th NOVEMBER, AFTER THE END OF FY |
BOOKS OF ACCOUNTS
- As discussed above, every LLP is required to maintain proper books of account on a cash basis or accrual basis and the report of same be submitted each year, on and before 31st March As per Income Tax Act, 1961, every LLP whose annual turnover exceeds Rs.40 lakhs or whose capital contribution exceeds Rs.25 Lakhs, are required to get their books of account audited by a Practicing Chartered Accountant.
- In case, the LLP fails to comply with the above requirement, they shall be punished with a fine of at least Rs.25,000 and it can extend to Rs.5,00,000. Also, the designated partner, if found guilty, be punished with a penalty of Rs.10,000, which can be extended to Rs.1 Lakh for non-compliance.
SUMMARIZED ANNUAL COMPLIANCES AND PENALTY FOR NON-COMPLIANCE
TYPE OF FORM |
DUE DATE |
PENALTY FOR NO-COMPLIANCE |
| FORM 11 FOR ANNUAL RETURN | ON AND BEFORE 30th MAY, AFTER THE END OF FY |
THE ROC MAY ALSO INITIATE LEGAL PROCEEDING IN CASE OF CONSISTENT DEFAULT. |
| FORM 8 FOR FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | ON AND BEFORE 30th OCTOBER, AFTER THE END OF FY |
DUE DATE FOR ANNUAL COMPLIANCE
FAQs ON LLP COMPLIANCES
Q.: Why are LLPs required to comply with annual compliances?
LLP being a corporate entity registered under MCA, is bound by the legal rules and procedures as given in the LLP Act 2008. Thus, every LLP irrespective of its size has to file Annual returns giving details about its management and financial performance and any delay in any of the compliance, would welcome heavy penalties from the government.
Q.: WHAT BENEFITS COULD BE REAPED BY COMPLYING WITH ANNUAL COMPLIANCES?
Complying with the annual compliances, would relieve the LLP from heavy penalties and frequent government interventions. Compliance would reduce certain legal regulations and day to day interference from authorities.
Q.: What are the ROC Compliances applicable for an LLP?
- Filing of annual return in Form 11 and Statement of Solvency in Form 8.
- Communication in respect of change in the registered office of LLP.
- Any change in the partnership like appointment, death or insolvency of Partners.
- any change in composition of designated partners or their DIN.
- Any change in the Capital Contribution of partners of LLP
- Any alteration in Name and Main objects of the LLP.
Q.: What are the relaxations provided to LLP?
LLP are provided with many relaxations in terms of exemptions from compulsory maintenance of books of accounts, statutory registers, annual general meeting and flexible tax rates. There is no restriction on conducting AGM once in a year.