Income Tax Audit Applicability & Application in India
Table of Contents
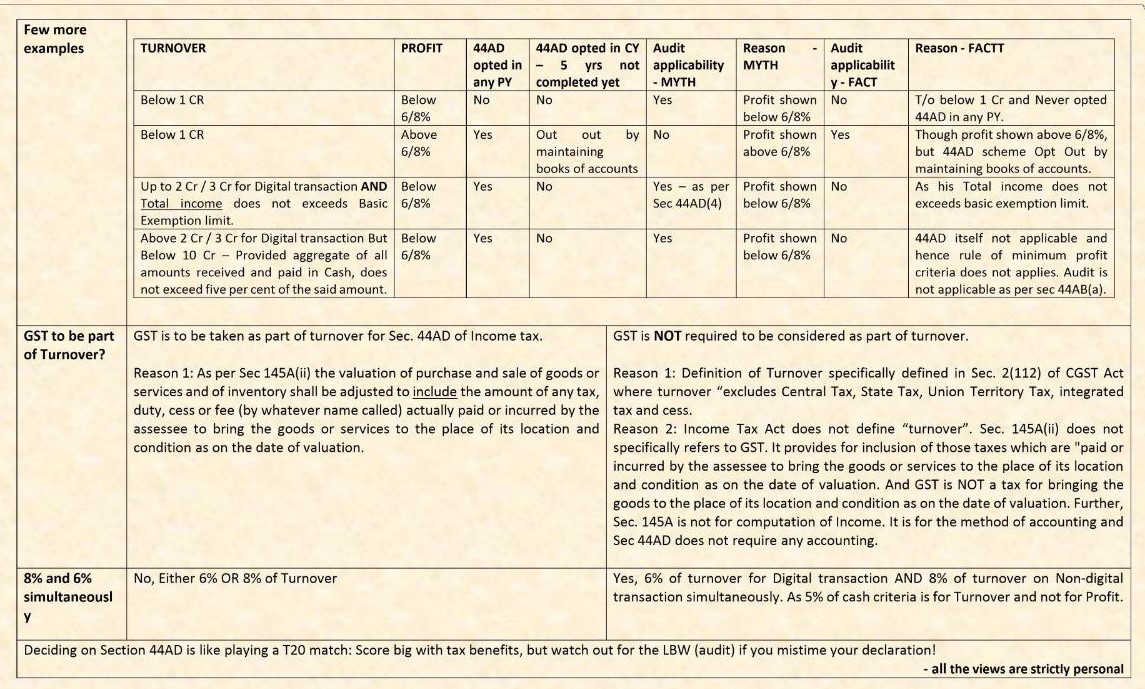
Myth vs Facts – Decoding Tax Audit u/s 44AB(e):44AD

| Nature of Business or Profession | When audit is Mandatory? |
Business loss |
|
| In case of loss from carrying on of business and not opting for presumptive taxation scheme | Total sales, turnover or gross receipts exceed Rs 1 Crore |
| If taxpayer’s total income exceeds basic threshold limit but he has incurred a loss from carrying on a business (not opting for presumptive taxation scheme) | In case of loss from business when sales, turnover or gross receipts exceed 1 Crore, the taxpayer is subject to tax audit under 44AB |
| Carrying on business (opting presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD) and having a business loss but with income below basic threshold limit | Tax audit not applicable |
| Carrying on business (presumptive taxation scheme under section 44AD applicable) and having a business loss but with income exceeding basic threshold limit | Declares taxable income that is less than the limitations set by the presumptive tax scheme but more than the basic threshold limit. |
All about Presumptive Taxation Scheme us 44AD, 44ADA and 44AE


Quick Comparison: Statutory Audit vs. Tax Audit

| Aspect | Statutory Audit | Tax Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Governing Act | 📌 Companies Act, 2013 (Sec 139-147) | 📌 Income Tax Act, 1961 (Sec 44AB) |
| Applicability | 📌 Mandatory for all registered companies, irrespective of turnover | 📌 Applicable to Companies, LLPs, Partnership Firms, and Individuals if turnover/professional receipts exceed the prescribed limit |
| Threshold Limit | 📌 No threshold; compulsory for all companies | 📌 Required if Business Turnover/Professional Receipts exceed the threshold (Refer attachment for limits) |
| Purpose | 📌 Ensures fairness, reliability, and transparency in financial statements | 📌 Ensures accurate tax reporting and proper maintenance of books |
| Due Date | 📌 Within 6 months of financial year-end, before AGM | 📌 Due date for filing report: 30th September of the assessment year |
| Consequences of Non-Compliance | 📌 Company Penalty: ₹25,000 – ₹5,00,000 📌 Officers in Default: ₹10,000 – ₹1,00,000 fine OR up to 1-year imprisonment |
📌 Penalty: Lower of 0.5% of turnover or ₹1,50,000 |
We are transparency and financial discipline. Recognition under the Income Tax Bill 2025 will enhance compliance and accountability in financial reporting.
**********************************************************
If this article has helped you in any way, i would appreciate if you could share/like it or leave a comment. Thank you for visiting my blog.
Legal Disclaimer:
The information / articles & any relies to the comments on this blog are provided purely for informational and educational purposes only & are purely based on my understanding / knowledge. They do noy constitute legal advice or legal opinions. The information / articles and any replies to the comments are intended but not promised or guaranteed to be current, complete, or up-to-date and should in no way be taken as a legal advice or an indication of future results. Therefore, i can not take any responsibility for the results or consequences of any attempt to use or adopt any of the information presented on this blog. You are advised not to act or rely on any information / articles contained without first seeking the advice of a practicing professional.
