Common Reasons for GST Notices, Sending & Compliance
Table of Contents
Common Reasons for GST Notices, Sending & Compliance
GST notices are official communications issued by GST authorities for reasons such as non-filing of returns, discrepancies, ITC mismatches, or other compliance issues. They require timely responses to avoid penalties or adverse actions. GST is based on self-assessment and self-certification, requiring taxpayers to comply proactively. Notices under GST are official communications from authorities to seek compliance or clarify discrepancies. Failure to respond within the stipulated time can lead to penalties, prosecution, or cancellation of registration. GST notices are official communications from GST authorities under the CGST Act, issued for reasons such as Non-filing of returns, Discrepancies in returns, ITC mismatches, Short payment of tax, Registration issues. & Timely response is crucial to avoid penalties, interest, or even cancellation of registration.
Common Reasons for GST Notices
- Failure to obtain GST registration when liable.
- Delay in filing GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B for more than six months.
- Mismatch between GSTR-1 & GSTR-3B or with e-way bill data.
- Excess ITC claims or refund claims (with or without intent to defraud).
- Non-payment or short payment of GST.
- Anti-profiteering violations (not reducing prices after GST rate cuts).
- Non-submission of information returns.
Mode of Sending GST Notices (Sec. 169(1), CGST Act, 2017) :
GST notices may be communicated to the taxpayer through the following lawful channels:
- Hand Delivery: Directly to the taxpayer or via a messenger, including courier. & Can be delivered to a representative (manager, advocate, family member, etc.).
- Registered Post / Speed Post / Courier: Sent with acknowledgement due to the last known business address of the taxpayer.
- Email Communication: Sent to the email address provided at the time of registration, as updated from time to time.
- GST Portal: Made available online after logging in to the taxpayer’s account.
- Publication in Regional Newspaper: Published in a newspaper circulated in the locality of the taxpayer, based on the last known residential address.
- Affixing at Last Known Place of Business or Residence: Notice may be affixed at a prominent place at the taxpayer’s last known business/residential address. If deemed unreasonable, notice may be affixed on the noticeboard of the concerned GST office as a last resort.
Notices can be served via Hand delivery, registered/speed post, courier, Email registered on GST portal, Upload on GST portal, Newspaper publication or affixture at last known address The taxpayer is required to act only on notices issued through the above lawful modes. Notices received through any other means are not legally enforceable and need not be acted upon. Important Forms in SCN Process
- DRC-01 – Summary of demand with SCN.
- DRC-01A – Pre-SCN intimation (chance to pay and avoid penalty).
- DRC-02 – Statement in lieu of full SCN for subsequent periods.
- DRC-03 – Payment of tax, interest, penalty.
- DRC-04 – Acknowledgment of payment.
- DRC-05 – Intimation of conclusion of proceedings.
- DRC-06 – Reply to SCN.
- DRC-07 – Adjudication order summary.
Situations Where SCN is Issued & Forms
| Situation | Form |
| Denial of Composition Scheme | GST-CMP-05 |
| Cancellation of Registration | GST-REG-17 |
| Rejection of Revocation of Cancellation | GST-REG-23 |
| Cancellation of Provisional Registration | GST-REG-27 |
| Disqualification of GST Practitioner | GST-PCT-03 |
| Rejection of Refund Claim | GST-RFD-08 |
| Best Judgment Assessment | GST-ASMT-14 |
| Demand for Tax (General) | GST-DRC-01 |
| Under Section 73 | SCN for tax short paid without fraud |
| Section 74 | SCN for tax short paid with fraud |
| Under Section 76 | SCN for tax collected but not paid |
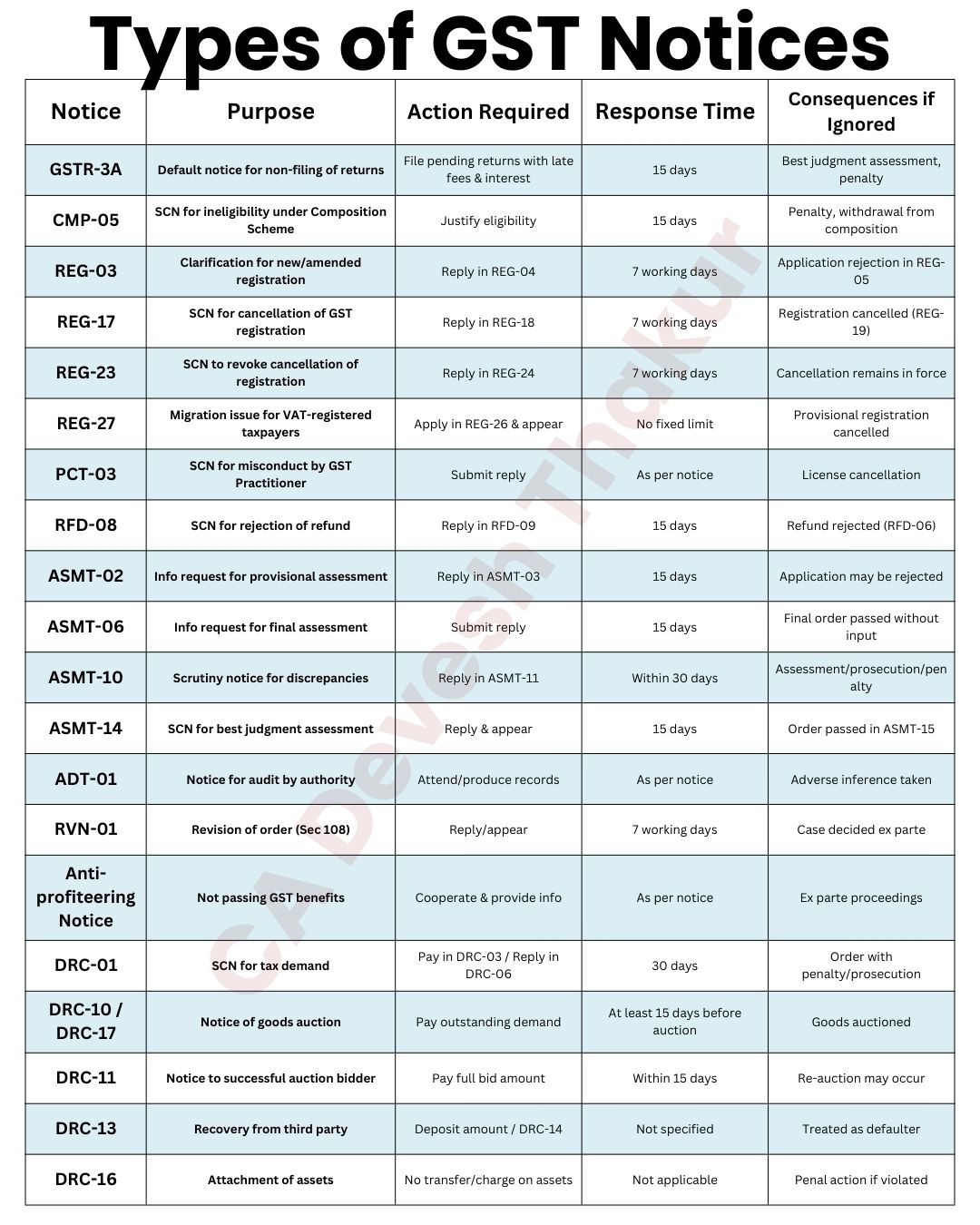
Types of Notices & Key Details :
Lists 19 common GST notices, their form numbers, sections/rules, purpose, action required, response time, and consequences. Examples:
- REG-03 – Clarification for new/amended registration : Reply in REG-04 within 7 working days; else application rejected.
- REG-17 – SCN for cancellation of GST registration : Reply in REG-18 within 7 working days; else registration canceled.
- GSTR-3A – Default notice for non-filing of returns : File pending returns within 15 days; else best judgment assessment.
- CMP-05 – SCN for composition scheme eligibility : Reply in CMP-06 within 15 days; else penalty and withdrawal.
- ASMT-10 – Scrutiny notice for discrepancies : Reply in ASMT-11 within 30 days; else ex-parte assessment.
- DRC-01 – SCN for tax demand : Reply in DRC-06 and pay via DRC-03 within 30 days; else order passed.
- Other notices include RFD-08 (refund rejection), ADT-01 (audit), RVN-01 (revision), and enforcement notices like DRC-10, DRC-11, DRC-13, DRC-16 for auction, recovery, and attachment.
GST Notice Compliance Checklist
1) Identify & Calendarise
- Capture Form No. (e.g., GSTR‑3A, ASMT‑10, DRC‑01, REG‑17) and issuing section/rule.
- Read the notice fully—facts, discrepancy points, documents asked, and due date.
- Create a compliance calendar entry with an owner and deadline (keep a 2–3 day buffer).
2) Retrieve from GST Portal
- Login → Services → User Services → View Additional Notices/Orders; download the notice and annexures.
- Verify DIN/Document ID and service date for limitation tracking.
3) Diagnose the Issue
- Classify: non‑filing, ITC mismatch, short payment/refund rejection, registration deficiency, audit.
- Map each point to source data (returns, ledgers, e‑way bills, books).
4) Gather Evidence
- GSTR‑1, GSTR‑3B, 2A/2B reconciliation, purchase/sales invoices, e‑way bill reports.
- PMT‑06 challans, credit/debit notes, refund working papers.
- Reconciliation sheets (returns vs books; 2B vs 3B).
5) Use the Correct Reply Form (standard timelines as per law/notice)
- REG‑03 → reply in REG‑04 (7 working days); registration clarifications.
- REG‑17 → REG‑18 (7 working days); SCN for cancellation.
- REG‑23 → REG‑24 (7 working days); SCN for revocation of cancellation.
- GSTR‑3A → file pending returns (15 days); default/non‑filing.
- CMP‑05 → CMP‑06 (15 days); composition eligibility SCN.
- ASMT‑10 → ASMT‑11 (within 30 days / as per SCN); return scrutiny.
- ASMT‑14 → appear (order in ASMT‑15; 15 days); best‑judgement assessment.
- RFD‑08 → RFD‑09 (15 days); refund rejection SCN.
- ADT‑01 → attend/produce records (as per notice); audit u/s 65.
- DRC‑01 → reply in DRC‑06; pay via DRC‑03 (30 days); SCN for demand.
- DRC‑10 → pay as per DRC‑09 (as per notice); auction of goods.
- DRC‑11 → pay bid amount (within 15 days); successful bidder notice.
- DRC‑13 → deposit & reply in DRC‑14 (timeline not specified); third‑party recovery.
- DRC‑16 → no transfer/charge on assets (N/A); attachment and sale of assets.
6) Draft a Crisp, Evidenced Reply
- Address each discrepancy point with reconciliations and document proofs.
- If liability exists, pay via DRC‑03 and attach workings & challans.
- Request personal hearing where appropriate; quote DIN and mention authorised signatory.
7) File Online & Record Proof
- Upload reply in the prescribed form with e‑sign/DSC.
- Save Acknowledgement/ARN, submitted reply PDF, and diarise a follow‑up date.
8) Service of Notice (CGST Sec. 169) — Know Valid Modes
- Hand delivery, registered/speed post/courier, email, portal upload, newspaper publication, or affixture at last known address. Act on notices served only through these permitted modes.
9) Risk & Escalation
- Missing timelines can lead to ex‑parte orders, penalties (Sec. 122), prosecution, or cancellation.
- For complex/high‑value cases, engage a CA and consider appeal within limitation.
Closing the Loop on GST Notice Compliance
With the ongoing digitalization of GST processes, the system is designed to minimize physical documentation and personal interaction with the Department. All replies to GST notices can be submitted online via the GST portal. Key Points
- Payment of Tax and Interest: If a notice involves tax or interest liability, payment must be made in the prescribed form and manner before submitting the reply.
- Submission of Reply: Replies must be submitted in the requisite form, along with any supporting documents, to the issuing tax authority. Replies can be filed using a digital signature (DSC) or e-signature of the authorized personnel or the taxpayer.
- Authorisation of Representatives: A taxpayer may authorize another representative to handle GST notice matters by issuing a Letter of Authorization. The authorized representative can reply to notices and take necessary actions on behalf of the taxpayer.
- Consequences of Non-Compliance: Failure to respond within the stipulated time can attract penalties, prosecution, and further proceedings under GST law. It is strongly advisable to comply timely and remain on the “right side of the law” to avoid adverse consequences.
GST Notice Compliance
All replies must be filed online on GST portal using prescribed forms. Payment of tax/interest (if applicable) must precede reply submission. Taxpayers can authorize a representative via Letter of Authorization. & Non-response leads to penalty, prosecution, and further proceedings. Read SCN line by line; note GSTIN, tax period, allegations, sections cited. Discuss with client; collect invoices, ITC details, e-way bills. Draft reply addressing each allegation; quote law and case precedents. Attach annexures for calculations, classification notes, case laws. Submit reply online in DRC-06 and keep acknowledgment.
Key Sections & Their Focus GST Notice Compliance
- Section 73 – Tax not paid/short paid/ITC wrongly availed (without fraud).
- Time Limit: SCN within 2 years 9 months; order within 3 years.
- Penalty: 10% of tax or ₹10,000 (whichever higher).
- Relief: Zero penalty if paid before SCN or within 30 days of SCN.
- Section 74 – Tax not paid/short paid due to fraud or suppression.
- Time Limit: SCN within 4 years 6 months; order within 5 years.
- Penalty: 100% of tax.
- Relief: 15% penalty if paid before SCN; 25% within 30 days of SCN; 50% within 30 days of order.
- Section 76 – Tax collected but not paid.
- Time Limit: No limit for SCN; order within 1 year of SCN.
- Penalty: Equal to tax amount (100%).
- No relief options.
Comparison of Sections 73, 74 & 76
| Aspect | Section 73 (No Fraud) | Section 74 (Fraud/Suppression) | Section 76 (Tax Collected but Not Paid) |
| Nature of Case | Tax not paid / short paid / ITC wrongly availed or utilized without fraud or willful misstatement | Tax not paid / short paid / ITC wrongly availed or utilized due to fraud, willful misstatement, or suppression | Tax collected from recipient but not paid to Govt |
| SCN Issue Timeline | Within 2 years 9 months from due date of Annual Return | Within 4 years 6 months from due date of Annual Return | No time limit prescribed |
| Order Passing Timeline | Within 3 years from due date of Annual Return | Within 5 years from due date of Annual Return | Within 1 year from date of SCN |
| Penalty Structure | 10% of tax or ₹10,000 (whichever higher) | 100% of tax | Equal to tax amount (100%) |
| Relief Options | – Before SCN: No penalty |
- Within 30 days of SCN: No penalty | – Before SCN: 15% penalty
- in case Within 30 days of SCN: 25% penalty
- Within 30 days of order: 50% penalty | No relief options available | | Forms Used | DRC-01 (SCN), DRC-03 (Payment), DRC-06 (Reply) | DRC-01, DRC-03, DRC-06 | DRC-01, DRC-03, DRC-06 | | Interest | Payable under Section 50 | Payable under Section 50 | Payable under Section 50
Penalty Relief Opportunities
- Section 73:
- Before SCN → No penalty.
- Within 30 days of SCN → No penalty.
- under Section 74:
- Before SCN → 15% penalty.
- i case Within 30 days of SCN → 25% penalty.
- Within 30 days of order → 50% penalty.
**********************************************************
If this article has helped you in any way, i would appreciate if you could share/like it or leave a comment. Thank you for visiting my blog.
Legal Disclaimer:
The information / articles & any relies to the comments on this blog are provided purely for informational and educational purposes only & are purely based on my understanding / knowledge. They do noy constitute legal advice or legal opinions. The information / articles and any replies to the comments are intended but not promised or guaranteed to be current, complete, or up-to-date and should in no way be taken as a legal advice or an indication of future results. Therefore, i can not take any responsibility for the results or consequences of any attempt to use or adopt any of the information presented on this blog. You are advised not to act or rely on any information / articles contained without first seeking the advice of a practicing professional.