OVERVIEW THE MAIL ORDER BUSINESS IN INDIA
Table of Contents
OVERVIEW THE MAIL ORDER BUSINESS IN INDIA
What is Mail Order Business?
Mail Order Business : A mail order business sells goods directly to customers through catalogues, advertisements, or printed material, where the orders are placed via post, phone, or email, and goods are delivered by courier or postal services. It usually operates without an online marketplace. Example: A company that sends printed catalogues to customers who then order via email or phone.
A mail order business is a retail business model where merchandise is sold by accepting and fulfilling customer orders primarily through mail or remote communication methods without the need for a physical retail store.
- Customers receive a product catalogue either in printed form or online, browse through it, select the products they want, and place their orders via mail, telephone, fax, email, or through an online store. The goods are then dispatched and delivered to the customer’s address by postal or parcel services.
- For mail order operations, GST registration is mandatory irrespective of turnover if you are selling through an e-commerce operator or electronically supplying goods or services.
- Details required for registration in GST: Pan card, Aadhar Card,Proof of business registration , identity and proof of partners,Bank Account details with cancelled cheques, Digital Photographs, Details of Goods to be sold etc. GST Registration Requirement Mandatory before commencing business, irrespective of turnover (Section 24). & taxpayer must apply in Form GST REG-09 at least 5 days prior to business commencement.
- For mail order business, especially if selling through e-commerce platforms, note that you may also be liable for Tax Collected at Source compliance handled by the platform but critical for your accounting and reporting.
E-Commerce Operator
- An e-commerce operator is defined under the GST Act (Section 2(45)) as any person who owns, operates, or manages a digital or electronic platform for electronic commerce — i.e., an online platform facilitating sale of goods or services. Examples: Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra, Meesho, etc. E-commerce operators are required to collect TCS (Tax Collected at Source) under Section 52 of the CGST Act.
Key Difference Mail Order Business Vs E-Commerce Operator
| Basis | Mail Order Business | E-Commerce Operator |
| Platform | Offline / Physical catalogues | Online / Digital platform |
| Intermediary Role | Direct sale by supplier | Facilitates sales between suppliers and buyers |
| GST Implication | Regular taxpayer | Operator must collect TCS u/s 52 |
| Customer Interaction | Through mail, phone, or physical order forms | Through an app or website |
Mail Order Business ≠ E-Commerce Operator. They are distinct business models, though both involve remote selling to customers.
Where will the Goods be stored in case Mail Order Business?
- A self-owned or leased storage facility where your business manages inventory, packing, and shipping.
- A third-party warehouse or fulfillment center operated by logistics/3PL service providers who store, pick, pack, and ship orders on your behalf.
- E-commerce marketplace facilities (like Amazon FBA or Flipkart Fulfillment) if selling via those platforms, where inventory is stored at their dedicated centers.
| Tax Aspect | Description | Details/Rate Examples |
| Property Tax | Levied by local municipal bodies on industrial/commercial property used for warehousing. | Rates vary by city/state; typical industrial property tax ranges from 0.1% to 1.5% of property value or assessed rental value; calculated via unit area, capital value, or annual rental value systems depending on locality. |
| GST | Applicable on warehousing services as a taxable supply under service tax regime. | Standard GST rate of 18% on warehousing and storage services; input tax credit available. |
| Income Tax | Rental income from warehousing is taxable under income tax; if used for own business, expenses deductible. | Rental income taxed as income from house property or business income; deductions allowed for municipal taxes, depreciation, interest on loans, and maintenance. |
BASIC REQUIREMENT DETAILS IN A MAIL ORDER BUSINESS :
- Supplier Details: Name, address, and GSTIN of the business issuing the invoice.
- Invoice Number and Date: Unique, consecutive invoice number and clear invoice date.
- Recipient Details: Name, address, and GSTIN (if registered). For supplies over INR 50,000, recipient information is mandatory even if unregistered.
- Product/Service Details: Description, quantity, unit price, total value, and HSN/SAC codes for goods/services.
- Shipping & Billing Address: Required for delivered goods, helps determine place of supply (affects CGST/SGST/IGST applicability).
- Tax Details: Rates and amounts for CGST, SGST/UTGST, and IGST, calculated on taxable value.
- Additional Notes: Mention of reverse charge (if applicable), signature of authorized signatory.
- Other Requirements: For e-commerce/mail order, include reference to the e-commerce operator if applicable, especially for COD or TCS transactions.
How COD Works in Practice under a mail order business invoice?
Customers place orders and select COD during checkout. The product is shipped to the customer via a courier or logistics partner. The courier collects payment (usually in cash, but sometimes by card or UPI) at the time of delivery. The collected amount is then remitted to the seller by the courier company, typically after deducting service charges and settling on a periodic basis (daily or weekly). Returns or rejections are handled by refunding or not collecting payment, with proper reconciliation between the seller and courier for inventory and settlements.
GST Taxation a mail order business invoice?
GST is chargeable on the taxable value of goods supplied even in COD orders, and the supplier must issue a GST-compliant invoice at the time of supply or delivery. E-commerce operators (platforms) facilitating sales are required to deduct Tax Collected at Source at 1% on the net value of taxable supplies sold through them, including COD sales, and remit it to the government. COD settlements are taxable at the time of supply, not when cash is received
Customs taxation a mail order business invoice
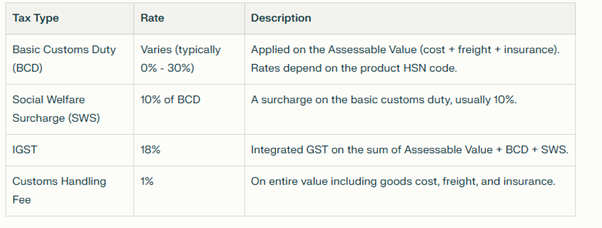
- All imported goods must be declared, and customs valuation will be based on CIF (Cost + Insurance + Freight) value.
- Types of customs duties include Basic Customs Duty (BCD), Social Welfare Surcharge (SWS), Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST), and any applicable additional duties.
TCS Procedure:
In the case of GST TCS for a mail order business conducted through an e-commerce platform, the credit for TCS is given to the supplier (the seller/vendor of goods or services). Here is how the mechanism works:
- The e-commerce operator collects TCS at the rate of 1% on the net value of taxable supplies made through its platform.
- The operator deposits this TCS amount to the government and files monthly returns (Form GSTR-8) detailing the tax collected.
- The GST portal credits the TCS amount to the electronic cash ledger of the supplier on whose behalf the tax was collected.
- The supplier can then utilize this TCS credit to offset their output GST liability while filing their GST returns.
- TCS is essentially a method of tax collection, and the benefit of the tax paid as TCS accrues to the supplier making the sales, not the operator collecting the tax.
Who deducts TCS and from whom?
- Deducted by the e-commerce operator (the platform owner facilitating the sale, e.g., Amazon, Flipkart).
- The e-commerce operator deducts TCS at 1% on the net value of taxable supplies made through its platform.
- The TCS is deducted from the payments made to the supplier or seller of goods or services through that platform.
- Essentially, the e-commerce operator collects TCS from the supplier by deducting it from the amount payable to the supplier.
Record Keeping a mail order business
Record-Keeping for Catalogue-Based Sales : You must maintain:
- Customer-wise sales register (invoice, dispatch details).
- Inventory records for each SKU.
- Payment reconciliation for COD & online receipts.
- Purchase register (for imports).
- Tax payment and return filing data.
- Retention period under GST = 6 years from the end of the financial year.
ACCOUNTING TREATMENT FOR TCS DEDUCTIONS: IMPORT OF SMALL GOODS:
- Import of goods attracts Basic Customs Duty (BCD) + IGST + Social Welfare Surcharge, based on product classification HSN code.
- You may claim input tax credit of IGST paid on imports, if registered under GST and goods are used for taxable supplies.
- Low-value consignments below INR 1,00,000 per shipment can be cleared under Courier Imports (Courier Imports Regulations, 2010) for faster clearance.
**********************************************************
If this article has helped you in any way, i would appreciate if you could share/like it or leave a comment. Thank you for visiting my blog.
Legal Disclaimer:
The information / articles & any relies to the comments on this blog are provided purely for informational and educational purposes only & are purely based on my understanding / knowledge. They do noy constitute legal advice or legal opinions. The information / articles and any replies to the comments are intended but not promised or guaranteed to be current, complete, or up-to-date and should in no way be taken as a legal advice or an indication of future results. Therefore, i can not take any responsibility for the results or consequences of any attempt to use or adopt any of the information presented on this blog. You are advised not to act or rely on any information / articles contained without first seeking the advice of a practicing professional.
