Mandatory LLP Annual Compliance’s
Table of Contents
LLP Annual Compliance’s
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a business entity that includes the characteristics of a partnership and a company. The Ministry of Corporate Affairs’ Registrar of Companies regulates LLPs. A limited liability partnership (LLP) is a legal entity that exists independently of its partners and has a perpetual succession. The following are some of the key advantages and forces that LLPs have:
- The ability to open a bank account.
- It is a legal body with its own right and Obligation
- The ability to hire employees.
- Assets that are movable, immovable, tangible, or intangible are purchased, sold, and held.
- Ability to sue and be sued.
- The ability to enter into some kind of legal agreement.
All LLPs are expected to maintain compliance and file such statutory filings with the government each year, in accordance with the powers. The main compliance requirements for an LLP are discussed in this article.
It’s not easy to run a business, whether it’s an LLP, an OPC, or a private limited company. A significant amount of money, time, and dedication is needed. Formalities, registration efforts, GST filings, and plenty of other considerations will make your head spin.
What is an LLP?
- A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a legal entity that is registered with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
- There must be two people in order to constitute an LLP one of them is must be an Indian citizen and resident of India.
- Each financial year, the partners in an LLP should be responsible for keeping accurate books of accounts, filing an Income Tax Report, and filing an annual return with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
Benefits of a Limited Liability Partnership include:-
- LLP, one partner is not responsible or liable for the wrongdoing or negligence of another partner.
- An LLP’s partners have the authority to run the business directly.
- The owners of an LLP have limited liability rights.
- If the number of Partners is reduced to less than two, the single partner will always find a new Partner to fill the vacancy.
- After incorporation, an LLP may have an unlimited number of partners.
- If an LLP has only one partner, there is time to find a new one before the LLP is dissolved.
- It is a legal body with its own right.
- An LLP will raise funds from partners, banks, and NBFCs, and its assets and liabilities are different from those of the promoters.
Also read :
Checklist for LLP Companies’ Statutory Compliance
-
- Every Financial Year, all LLPs registered with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) in India must file Statements of Accounts and Annual Returns.
- Even if the LLP has done business or made a profit, it is required to file a return. When you own an LLP, you must comply with three requirements.
-
-
- Filing of Annual Return
- Books of Account
- Filing of Income Tax Returns
-
Annual Return to a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
An LLP’s annual return, also known as Form 11, is a summary of its partners. It also indicates whether or not there has been a change of management. Within 60 days of the end of a financial year, every LLP must file an Annual Return in Form 11 with the Registrar. That is, the Annual Return must be filed annually by the 30th of May.
Also read : Mandatory LLP Annual compliances
Filing of Annual Accounts, Statement of Accounts, Profit and Loss Statement, and Balance Sheet
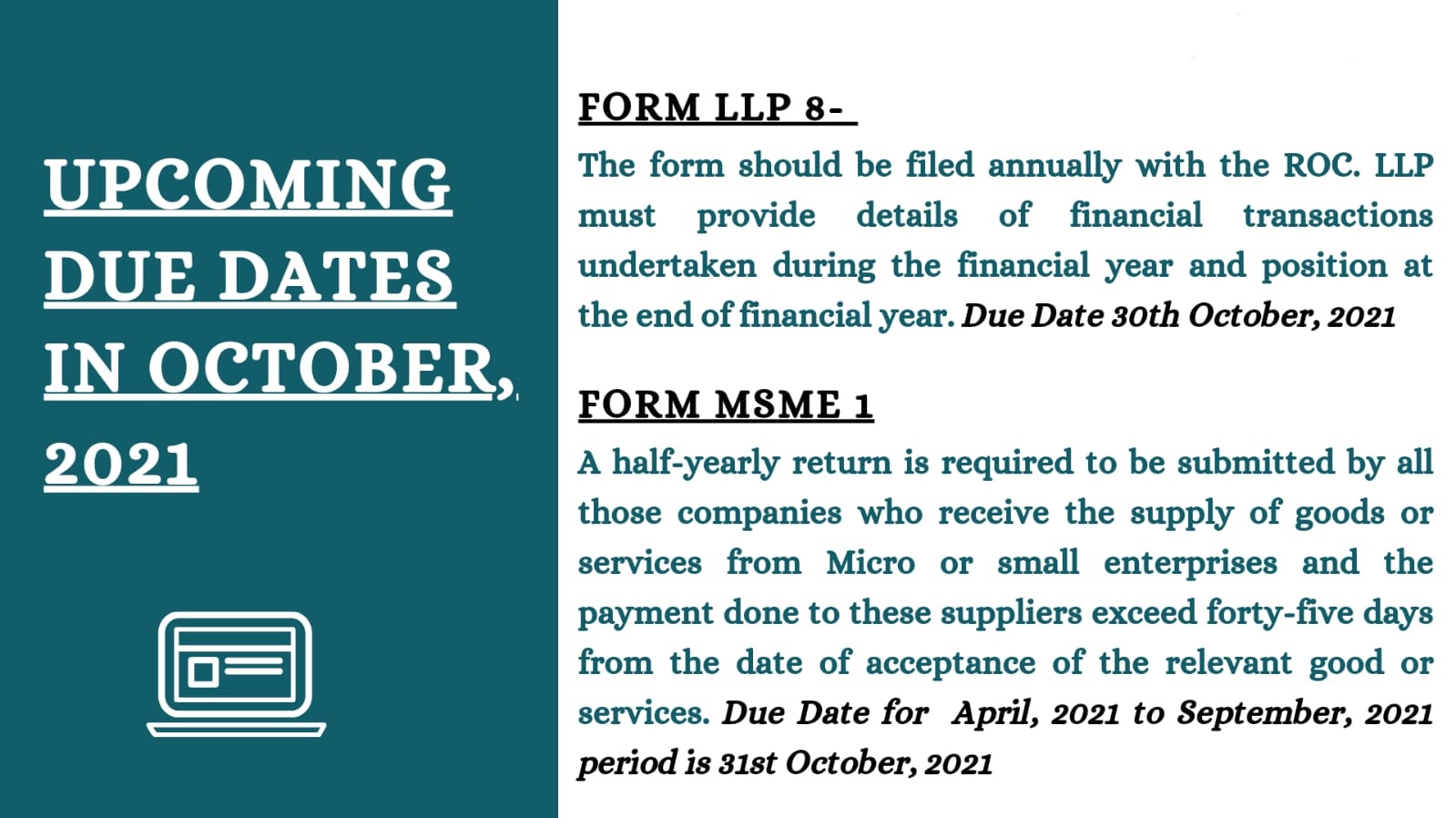
All LLPs must maintain their books of accounts in the double entry system. Every year ending on March 31st, they must also prepare a Statement of Solvency (Accounts). LLP Form 8 should be registered with the Registrar of Companies on or before the 30th of October each year for this reason.
Filing of Income-tax
If your LLP has a turnover of more than Rs.40 lakhs or a capital of more than Rs.25 lakhs, you must file income tax and get the books of account audited by a Chartered Accountant. The deadline to file an LLP’s tax return, which is expected to have his books verified and examined, is September 30th. The deadline for filing the tax for LLPs where a tax audit is not required is July 31st.
Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs) that are necessary to file Form 3CEB (LLPs that have engaged in international transactions) have until November 30th to complete their tax filing. LLPs can use Form ITR 5 to file their income tax returns. With the aid of the digital signature of the chosen spouse, the form could be submitted electronically through the income tax website. LLP tax payments may be made either physically or electronically via selected banks.
| Forms to be filed | Last date for filing | Extended due date | |
| Annual Return (Form 11) | 30-05-2021 | NA | |
| Accounts (Form 8) | 30-10-2021 | NA | |
| Income Tax Return | Last date for filing | Extended due date | |
| In case Audit is not required | 31-07-2021 | 30-09-2021 | |
| In Case Audit is required | 31-10-2021 | 30-11-2021 |
Books of Account
On a cash or accrual basis, all LLPs must keep proper books of account. Each year, by the 31st of March, the report must be completed and submitted in a timely manner. When the accounts books are required, they must be presented to the registered office. A Chartered Accountant must audit the accounts of LLPs with a turnover of more than Rs.40 lakhs or capital of more than Rs.25 lakhs.
Any LLP that fails to comply with the Act’s provisions can be fined a minimum of Rs.25,000 and a maximum of Rs.5,00,000. In addition, non-acquiescence could result in a penalty of between Rs.10,000 and Rs.1 lakh for the designated partner.
*The Income Tax Act requires an audit of accounts if the LLP’s annual revenue exceeds one hundred lakh rupees.
- Running a business, whether as a sole proprietorship, LLP, or a Private Limited Company, is a difficult job.
- It takes time, resources, and effort, and it necessarily requires knowledge of numerous regulatory and financial formalities.
- It is important to submit all forms and returns on time. If the Forms are not filed with the Registrar on time, there are severe penalties.
MANDATORY ANNUAL COMPLIANCES
| Form No. to be Filed | Due Dates | Late Fees for non-filling of Form-8 & Form-11 |
| 1. Form 11 (Annual Return of LLP) |
Within 60 days from the end of Every Financial Year | For LLP: Per day penalty of Rs. 100 till the filing is completed So for example: When the Form 11 and Form 8 of the LLP is not filed within the due dates and for example the delay is of 100 days for each form then the Government penalty fees will be:· The penalty amount ranges from Rs. 10,000 (i.e. @ Rs. 100 per day for 100 Days) in case of Form-11+The penalty amount ranges fromRs. 10,000 (i.e. @ Rs. 100 per day for 100 Days) in case of Form-8· For Designated Partner: The penalty amount ranges From Rs. 10,000 to Rs. 100,000· ROC can issue Notice to LLP and start the legal proceedings |
| 2. Form 8 Filing (Statement of Accounts & Solvency of LLP) |
Within 30 days from the end of 6 months from the closure of Every Financial Year |
MCA LLP Forms 3, 8, 11, and KYC Due Dates for FY 2020-21
MCA has communicated its decision via its “general circular bearing Number 06/2021 and dated May 3, 2021” to provide additional time for filling out certain forms that are due between April 1, 2021, and May 31, 2021, without any additional charge, as per the companies act 2013 and the LLP Act 2008. If an LLP was formed before October 1, 2020, it will be exempt from the tax.
- The LLP’s first financial year will end on March 31, 2021, and it will be required to file its Annual Return in “Form-11” on or before May 30, 2021, and its
- Form-8 (Declaration of Solvency) is to be filed on or before October 30, 2021, for the Financial Year 2020-21; however, the due date of “Form 11” has been extended til July 31, 2021 without any late fees, through the release of this General Circular.
Time-limit of LLP Forms under MCA for FY 2020-21
- Form-3 – It is to be filed within 30 days of the Incorporation of an LLP
- And Form-8 – It is to be filed on or before October 30, 2021
- Moreover Form-11 – It is to be filed on or before July 31, 2021
- Director KYC – It is t be filed on or before September 30, 2021
Frequently asked Question’s (FAQ’s) on LLP Compliance
-
Why LLP ROC Compliance is required?
-
- The LLP Act 2008 establishes the legal rules and procedures that govern the operation of LLPs.
- Every LLP, regardless of size, is required to file annual returns detailing its management and financial results.
- The ROC is a authorized govt department office under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs that monitors the compliance of limited liability partnerships (LLPs) that fall under its jurisdiction.
-
What are the 3 benefits of AMC for LLPs?
-
- Many LLPs are unable to meet filing deadlines and face significant penalties as a result.
- Any entrepreneur must concentrate on their company and delegate legal matters to capable and trustworthy professionals.
- AMC offers significant cost savings.
-
What are the ROC Compliances applicable for an LLP?
-
- There are the certain ROC forms filed by an LLPs is
| Mandatory Annual Compliance’s | |
| Form-11 | Annual Return of Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) |
| Form-8 | Statement of Account & Solvency |
| Frequently Forms used by the LLPs | |
| Form FiLLiP | Form for Incorporation of Limited Liability Partnership |
| Form-3 | Information with regard to limited liability partnership agreement and changes, if any, made therein |
| Form-4 | Notice of appointment, cessation, change in name/ address/designation of a designated partner or partner. and consent to become a partner/designated partner |
| Form-5 | Notice for change of name |
| Form-15 | Notice for change of place of registered office |
| Form-17 | Application and statement for conversion of a firm into Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) |
| Form-18 | Application and Statement for conversion of a private company/ unlisted public company into limited liability partnership (LLP) |
| Form-24 | Application to the Registrar for striking off name |
| Form-25 | Application for reservation/ renewal of name by a Foreign Limited Liability Partnership (FLLP) or Foreign Company |
| Form DIR-3 | Application for allotment of Director Identification Number |
| Form DIR-6 | Intimation of change in particulars of Director to be given to the Central Government |
-
What are the Compliance exemptions for LLP?
-
- In comparison to a private limited company, an LLP enjoys a number of advantages, including exemptions from the keeping of minute’s books, statutory registers, annual general meetings, and tax rates that are more flexible.
-
Is a Board meeting to be held for a Limited Liability Partnership?
-
- In an LLP, there are no directors; instead they are called as designated Partners who manage the LLP and are kept accountable for compliance.
- A Board of Directors meeting is usually associated with a Board meeting.
- In the case of an LLP company, a meeting of the Board of Partners is recommended.
-
Is Annual General meeting (AGM) applicable to an LLP?
-
- No, an LLP does not require an annual general meeting.
- The AGM is a once-a-year meeting of the Company’s Shareholders.
- An LLP does not have a concept of shareholding, so there will be no AGM.
-
Is it necessary to file Forms 8 and 11 even though no transactions occurred during the year?
- Even if no transaction occurs during the year, the forms must be filed to keep the LLP’s active status. This keeps the MCA informed of the LLP’s current state of affairs.
- you can also review : Complete understanding about LLP Compliances
**********************************************************
If this article has helped you in any way, i would appreciate if you could share/like it or leave a comment. Thank you for visiting my blog.
Legal Disclaimer:
The information / articles & any relies to the comments on this blog are provided purely for informational and educational purposes only & are purely based on my understanding / knowledge. They do noy constitute legal advice or legal opinions. The information / articles and any replies to the comments are intended but not promised or guaranteed to be current, complete, or up-to-date and should in no way be taken as a legal advice or an indication of future results. Therefore, i can not take any responsibility for the results or consequences of any attempt to use or adopt any of the information presented on this blog. You are advised not to act or rely on any information / articles contained without first seeking the advice of a practicing professional.