All About Striking off of Company
Table of Contents
Brief Introduction about Striking off of Company
- Running a corporation is not a cakewalk, sometimes the founders of the corporate take tough decisions to shut down the entity. During the last 3 years, nearly 3.8 lakh companies are struck off under the companies Act, 2013.
- Many companies find it difficult to undertake their operation under the Covid 19 pandemic. There are two ways for closing an organization, strike off and winding up of the corporate.
- Additionally, some businesses go for termination and removal of name from the ROC because it is considered as a viable option. Thus, in order to provide assist such companies, Companies Act provides for the process of striking off of the company under section 248 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- Here in this article, we are going to be specifically looking into the striking off companies under section 248, the process of Striking off under Companies Act, 2013, and therefore the documents required for strike off.
Meaning of Striking Off of Company
- In a layman’s language, it is said that strike off is withdrawing companies name from the Register of the corporate. the method of striking off under Companies Act, 2013 is more just like the closure or winding up of a corporation. the corporate no longer exists after striking off and it cannot operate thereafter.
Governing Section of Striking Off of Company

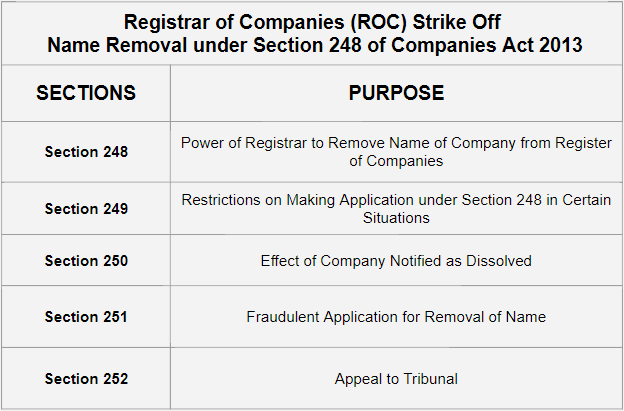
- Section 248 of the companies Act prescribes power to Registrar for removing the name of the corporate from the ROC. As per the section the Registrar has the right to strike off the company’s name.
- Firstly, on failure to commence the business within 1 year of incorporation.
- Secondly, the Registrar can remove the name if the corporate fails to hold business for 2 financial years and has not made an application for the status of a dormant company in accordance with the section 455 of Companies Act, 2013. So, a dormant company is basically a company which does not undertake any activity and is termed as an inactive company. There aren’t any accounting transactions regardless of the registration under the companies Act.
- Section 248 in clause 2 states that the corporate can on its own by special resolution file an application for removal of the name of the corporate from the ROC. Companies even have to comply with Companies (Removal of Names of Companies from the Register of Companies) Rules, 2016 for the method of striking off under the companies Act, 2013.
About Rule 4 of the Companies (Removal of Names of Companies from the Register of Companies) Rules, 2016
- Before the 2019 Amendment, there was a rule that a corporation can file an application for strike off in Form STK-2 providing it’s filed an overdue return form AOC-4 or AOC-4 XBRL together with Form MGT-7.
- the ROC issued a notification, asking some companies for submission of their overdue returns and also, in some cases, it was even accepting the strike-off application, without filling of overdue returns by the applicant company.
- Moreover, there was some type of discrepancy within the system, but after the 2019 amendment, the position is far clear.
- According to the amendment in Rule 4 of the companies (Removal of Names of Companies from the Register of Companies) Rules, 2016 in May 2019, companies cannot file the applying in form STK-2 unless the corporate has submitted the overdue returns in form AOC-4 or AOC-4 CBRL and Form MGT-7 up to the end of the twelvemonth.
- AOC-4 is the financial statement and therefore the MGT-7 is the annual return of the corporate.
- this implies that the corporate should file the annual return till the corporate conducted its business.
- It’s not mandatory to submit annual pending returns before striking off and therefore the company can proceed further without filing the annual return for the year within which they didn’t conduct business.
- Apart from this, the MCA decided to increase the fees for making striking off application and the same was increased to Rs. 10,000.
- This move was highly criticized because the Ministry has turned the incorporation fee to zero but the fee to exit has nearly doubled.
Modes of Striking Off- of Company
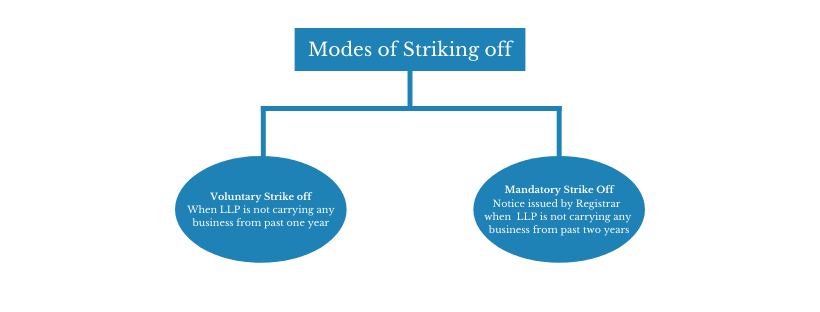
There are two modes for striking off a corporation in India under the companies Act-
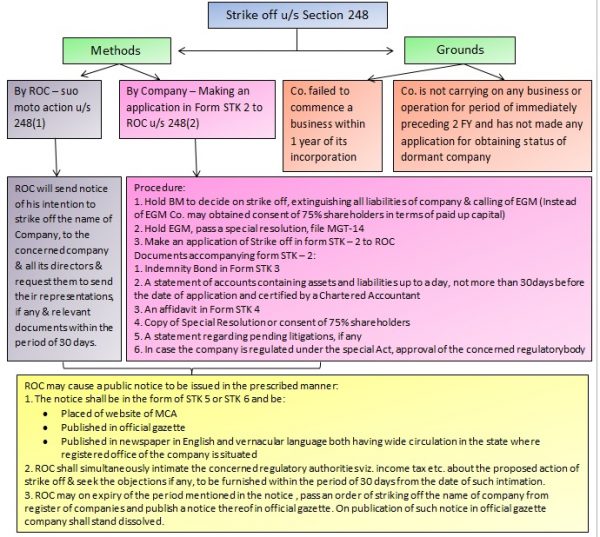
- Strike-off by Registrar of the corporate under section 248(1): This section gives power to the Registrar to strike off a corporation from the register of companies. this can be also the Suo-moto action on a part of Registrar.
- Registrar of company can issue notice to the businesses in form STK-1, intimating about the withdrawal of the name of the corporate from the Register of the corporate.
- This notice will inform the businesses about the removal. we will also call this process as compulsory removal of the name from the ROC.
Some of the grounds of striking off an organization include failure to commence business within one year of incorporation and not carrying business for 2 financial years and has not made an application for attaining a dormant company status.
- Striking off under Section 248(2): Under this, the Companies themselves apply for the strike off of their name from the ROC register. Such an application is required to be made in form STK-2 and the same be submitted only after the closure of their liabilities.
- They can do so if they fail to commence business or haven’t done any business for the last two financial years. This process can start by passing special resolution along with consent of 75% of the members.
In accordance with section 248(1) of the companies act 2013, the ROC follows the subsequent process of striking off under the companies Act-
- Firstly, the Registrar shall send notice to the corporate in form STK-1 for notifying about the withdrawal of the name from the ROC.
- Secondly, the ROC shall inspect the representation of the corporate. If the ROC isn’t satisfied with the representations, it can proceed further.
- There should be a publication of the said notice and therefore the same shall be available on the official MCA website, the official gazette. Finally, it should even be printed within the newspapers in English and a vernacular language.
- The ROC also needs to intimate the regulatory authorities having jurisdiction about the removal or striking off the corporate name. If the authorities want, they will raise an objection or issue within 30 days of the said notice.
- According to section 248(5) the ROC after the expiry of the time cross out the name and publish the notice within the Official Gazette. Then the corporate will stand dissolved on the publication of the notice within the Official Gazette.
- Before striking off the corporate, the Registrar shall ensure that the corporate has discharged all its liabilities and payments.
Process of Strike-off Voluntarily
- The company must hold a board meeting and passes a resolution. After this, the corporate can make an application for strike off and therefore the process of striking off under the companies Act will start.
- In the following step, the corporate should necessarily close all the liabilities.
- Lastly, the corporate conducts a general meeting of the shareholders by passing a resolution backed by 75% of the members. Thereafter the corporate can file form MGT-14 within 30 days.
Documents needed for Striking Off of Company
Companies must submit the subsequent documents together with the application for starting the method of striking off under the companies Act-
- Duly notarized Indemnity bond in the prescribed Form STK-3.
- Statement of liabilities or accounts consisting of the assets of the corporate together with the liabilities in form STK-8.
- An affidavit in Form STK 4.
- Certified Copy of Special Resolution, being duly signed by the directors.
- The statement stating about pending litigations of the corporate.
After-Effects of Dissolution
- According to section 250 of the companies Act, if an organization dissolves under section 248, they have to stop function immediately on the date mentioned within the notice of dissolution.
- Additionally, the certificate of incorporation also will stand cancelled.
Liabilities of Directors
- The obligations of the directors and other authoritative officers shall proceed and it’d be enforced as if the corporate isn’t dissolved.
Companies Ineligible for Strike Off
- According to Section 249 of the Act, no company can make an application under section 248(2) if it’s changed the name, shifted registered office from one state to a different, has made disposal of property, engaged in the other activity apart from necessary within the past three months.
- Companies cannot file an application if they need made an application for sanctioning a compromise or arrangement and therefore the matter isn’t yet decided. And
- Where the corporate is winded up in accordance with the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016.
Companies which cannot strike off under Section 248-
- Listed companies and companies which are delisted due to non-compliance of the listing regulations or agreements.
- Companies failed to respond to the notice served under section 248.
- Vanishing companies and corporations within which investigation is going on or pending and the proceedings are pending in Court.
- Companies which haven’t furnished the follow-up instructions on the reports under section 208.
- Lastly, section 8 companies.
Consequences of Non-Compliance of Company
- If a corporation fails to go with Section 455 of the Act and companies (Miscellaneous) Rules, 2014 i.e., filing of annual return within 30 days from the yr ending, the ROC will strike off the name of the corporate.
- Moreover, there’s punishment under section 450 if the corporate defaults to fits the necessities. Additionally, there’s a punishment for company, in addition because the directors, for violation of the companies Act.
Procedure of Revival of a Struck-Off Company:

Conclusion
- The process of striking off under Companies Act, 2013 could be a viable alternative for companies.
- it’s the only option for company searching for a mode for bringing the corporate to an end. the corporate and therefore the ROC both have the right to start the method.
- Striking off a corporation was brought good to encourage easy doing business together with ease in closure.
Also read : Compliance for Foreign Subsidiary Companies in India
**********************************************************
If this article has helped you in any way, i would appreciate if you could share/like it or leave a comment. Thank you for visiting my blog.
Legal Disclaimer:
The information / articles & any relies to the comments on this blog are provided purely for informational and educational purposes only & are purely based on my understanding / knowledge. They do noy constitute legal advice or legal opinions. The information / articles and any replies to the comments are intended but not promised or guaranteed to be current, complete, or up-to-date and should in no way be taken as a legal advice or an indication of future results. Therefore, i can not take any responsibility for the results or consequences of any attempt to use or adopt any of the information presented on this blog. You are advised not to act or rely on any information / articles contained without first seeking the advice of a practicing professional.