Latest Amendment in Tax Audit under section 44AB
Income Tax Audit Form No. 3CD amended by The Central Board of Direct Taxes through Notification No. 33/2018,
The new features of Form 3CD will be in effect from 20th August 2018 to incorporate further reporting requirements related to Goods and Service Tax (GST), Transfer pricing, Statement of Financial Transactions, Section 32AD, Income from other sources as referred to in clause (x) of sub-section (2) of section 56, Cash Receipt / Payment of More than 2 Lakhs from a single person in a day.
The following rules are made as under Income-tax Rules, 1962, namely:-
- These rules may be called the Income-tax (8th Amendment) Rules, 2018.
- Changes in Appendix II, in Form No. 3CD,-
- Under the serial number 4, there is a Requirement to furnish the GST No.
- in serial numbers 19 & 24, Section “32AD” has been added to allow the deduction in respect of investment in notified backward areas of Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Telangana, West Bengal.
- Under the serial number 26, clause (f) of section 43B is added which allows the liability towards Railways for use of their assets on an actual basis.
- After serial number 29,
- No. 29A is added for section 56(2)(ix) of the Act. to tax, the advance amounts received against the capital asset in the course of negotiation, but later forfeited and no transfer effected.
- It is worthwhile to be noted that any amount comes under this head then specifies the Nature of income and amount.
- No. 29B to show whether any amount is to be included as referred to in clause (x) of sub-section (2) of section 56 chargeable under the head ‘income from other sources
- It is worthwhile to be noted that any amount comes under this head then specify the Nature of income and amount.
- After serial number 30, Sr. No. 30A is added for section 92CE, According to this section any primary transfer pricing adjustments made in the case of an assessee, the assessee is required to make a secondary adjustment provided that:
- The given primary adjustment is more than 1 crore; and
- It also pertains to the assessment year on or after 1 April 2016.
Where such an amount is not recovered, then the balance should be treated as an advance given to AE and recovered along with the interest.
- No. 30B is added which provides that where the assessee has incurred expenditure during the previous year as an interest or of similar expenditure exceeding one crore rupees as referred to in sub-section (1) of section 94B.
It is noted that where the above provision follows, the assessee should provide the following:-
Amount of expenditure by way of interest or of similar nature incurred.
- Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization during the previous year.
- Expenditure as an interest or of similar nature as per (i) above which exceeds 30% of EBITDA as per (ii) above:
- Amount of interest expenditure brought forward as per section 94B.
- The Amount of interest expenditure carried forward as per section 94B.
- no. 30C is added for section 96 of the Act. to ascertain whether the assessee has entered into an impermissible avoidance arrangement where such agreement creates such rights between the parties, by misuse of the provision of the Act, which not created in the normal course between parties dealing at arm’s length.
It is noted that the assessee provide the following details if cover under the above provisions as follows:-
- Nature of the impermissible avoidance arrangement.
- Amount of tax benefit in the previous year arising to all the parties to the arrangement.
In serial number 31, Clause (ba), (bb), (bc) and (bd) has been included pertaining to section 269ST of the Act as follows:-
- “(ba) Particulars of each transaction where an amount received in aggregate of INR Two Lakhs from a person in a day or in respect of a single transaction or in respect of transactions during the previous year, where such amount is received other than by a Cheque or bank draft or any of the electronic clearing system. The following information is required as stated below:-
- Name, address, and PAN No. of the assessee;
- Nature of the transaction;
- Amount of receipt;
- Date of receipt;
- (bb) Particulars of each transaction where the amount received in aggregate of INR Two Lakhs from a person in a day or in respect of a single transaction or in respect of transactions relating to one event or occasion from a person, received by a cheque or bank draft, not being an account payee cheque or an account payee bank draft, during the previous year. The following information is required as stated below:-
- Name, address, and PAN No. of the assessee;
- Amount of receipt
- (bc) Particulars of each and every transaction payment made in an amount exceeding INR Two Lakhs in the aggregate to a person in a day or in respect of a single transaction or in respect of transactions relating to one event or occasion to a person, otherwise than by a cheque or bank draft or use any electronic clearing system through a bank account during the previous year. The following information is required as stated below:-
- Name, address and PAN of the payee;
- Nature of transaction;
- Amount of payment
- Date of payment.
- (bd) Particulars of each and every transaction payment made in an amount exceeding INR Two Lakhs in the aggregate to a person in a day or in respect of a single transaction or in respect of transactions relating to one event or occasion to a person, otherwise than by a cheque or bank draft or use any electronic clearing system through a bank account during the previous year. The following information is required as stated below:-
- Name, address and PAN of the payee;
- Amount of payment.
It is further advised to be noted that the Particulars at (ba), (bb), (bc) and (bd) are not required to provide if the amount is receipt by or paid to a Government company, a banking company, a post office savings bank, cooperative Bank.
- In sr. number 34, in place of item (b), the following Para shall be substituted as:-
Whether an assessee is required to furnish the statement of TDS or TCS. If the assessee is required for the above then he specifies the following below information’s:-
- Tax deduction & Collection Account Number
- Type of Form
- Whether the statement of TDS or TCS contains information about all details/transactions which are required to be reported
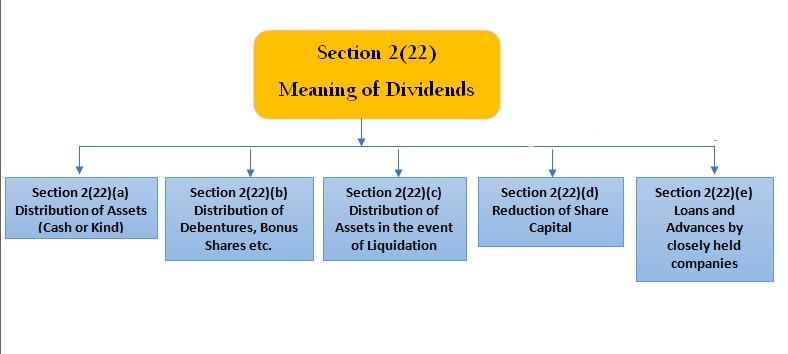
- serial number 36A is included for deemed dividend u/s 2(22)(e). It suggests that the assessee who holds not less than ten per cent voting power received by way of loan or advance provide the information regarding Amount and Date of Receipt.
- After serial number 41 and the entries relating thereto, the following shall be inserted, namely:-
Sr. No. 42 inserted in respect of form no. 61, 61A, 61B
The auditor must satisfy himself that all the required information is submitted, if not provided then ensure that same should be provided in Form 3CD.
- Form 61- it provides the detail of form 60. The transaction under rule 114B follows and document with that regard has been collected by the assessee without PAN, then assessee collects detail in Form 60.
- The Form 61A-Furnish the information regarding the transaction given under rule 114E implemented during the financial year.
- Form 61B- Statements of the Accounts which should be reported in accordance with FATCA and CRS for a calendar year.
- No. 43 inserted w.r.t. to country by country reporting under section 286 of the act.
Section 286 specifies the companies liable to comply with country by country reporting. They are requiring to complying with the reporting requirement of form 3CEAC and Form 3CEAD, wherever applicable.
The information required is stated below :
- Parent entity name
- Name of the alternate reporting entity (if applicable)
- Date of furnishing report
- No.44 inserted to provide the following information regarding the Break-up of expenditure of entities whether registered or not under the GST as follows:-
- Total expenditure incurred during the year.
- Expenditure relating to goods and services not liable to tax
- In case the expenditure of entities falling under the composition scheme
- Expenditure relating to the entities not registered in GST
Conclusion:
The liability of the Auditor is increased towards the requirement of documentation and verification towards the compliance of the provisions and rules of the Act.
THE DTC REPRESENTATION OF THE ICAI SUGGESTS ON TAX AUDIT UNDER INCOME TAX FOR THE AY 2020-21 :
In the light of the above and in the interests of the nation as a whole, it is humbly requested that the due date of filing of income U / S 139(1) for all assesses be extended to at least 31.03.2021 from the existing extended due date of 30.11.2020 for AY 2020-21. At the same time, the ‘defined date’ for filing tax audit reports shall be extended from 31.10.2020 to 28.02.2021 for AY 2020-21.
Furthermore, it is also desired that the online JAVA utility file ITR Form 5 & 6 be published at the earliest opportunity on the e-filing portal of the Income Tax Department to allow the assesses concerned to file their return of income within the specified timeframe.
Tax Audit Form Update for the AY 2024-25
- Central Board of Direct Taxes notifies the Tax Audit Form Update for the AY 2024-25 vide updating the Form schema releasees dated on 29th March 2024
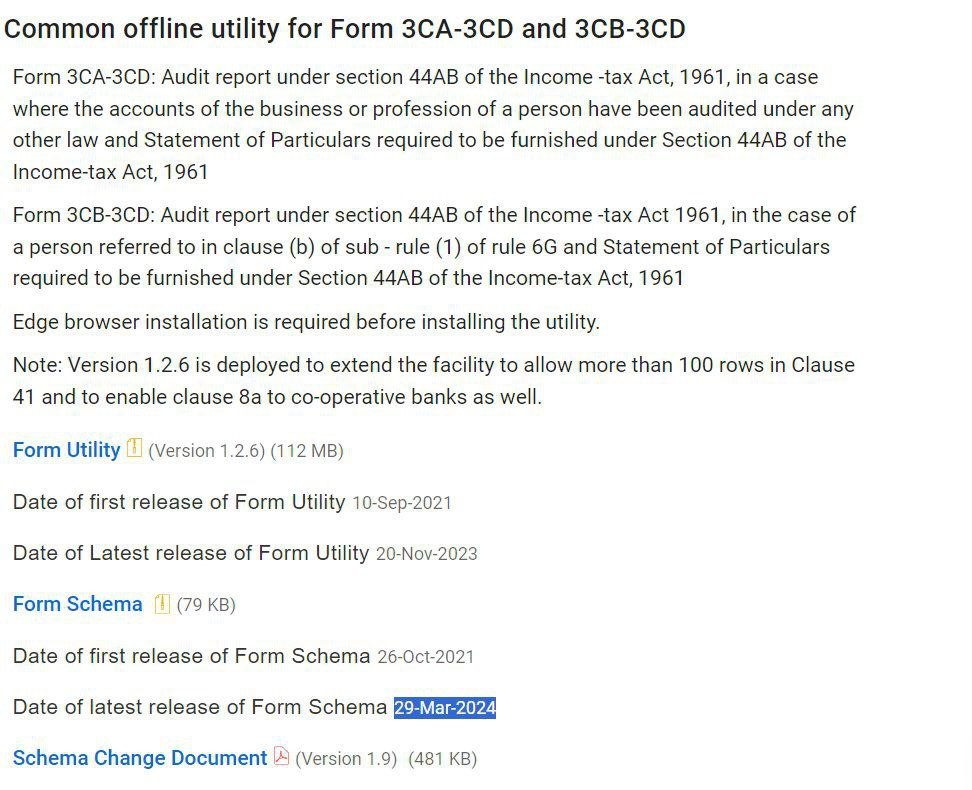
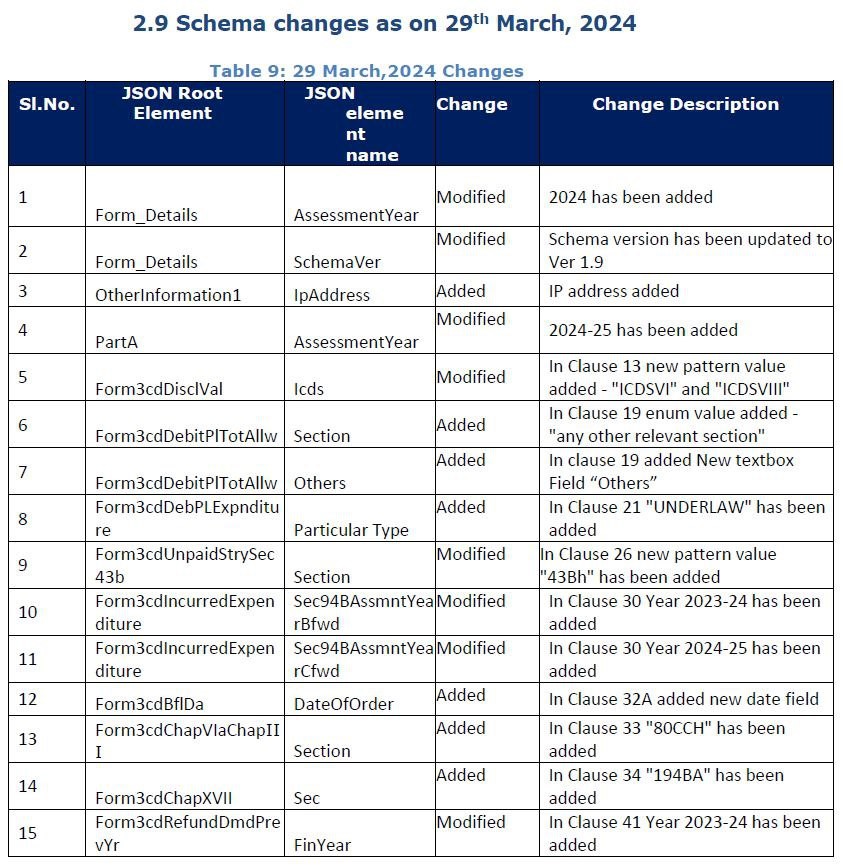
- Date of the latest release of Tax Audit Form Schema 29-Mar-2024
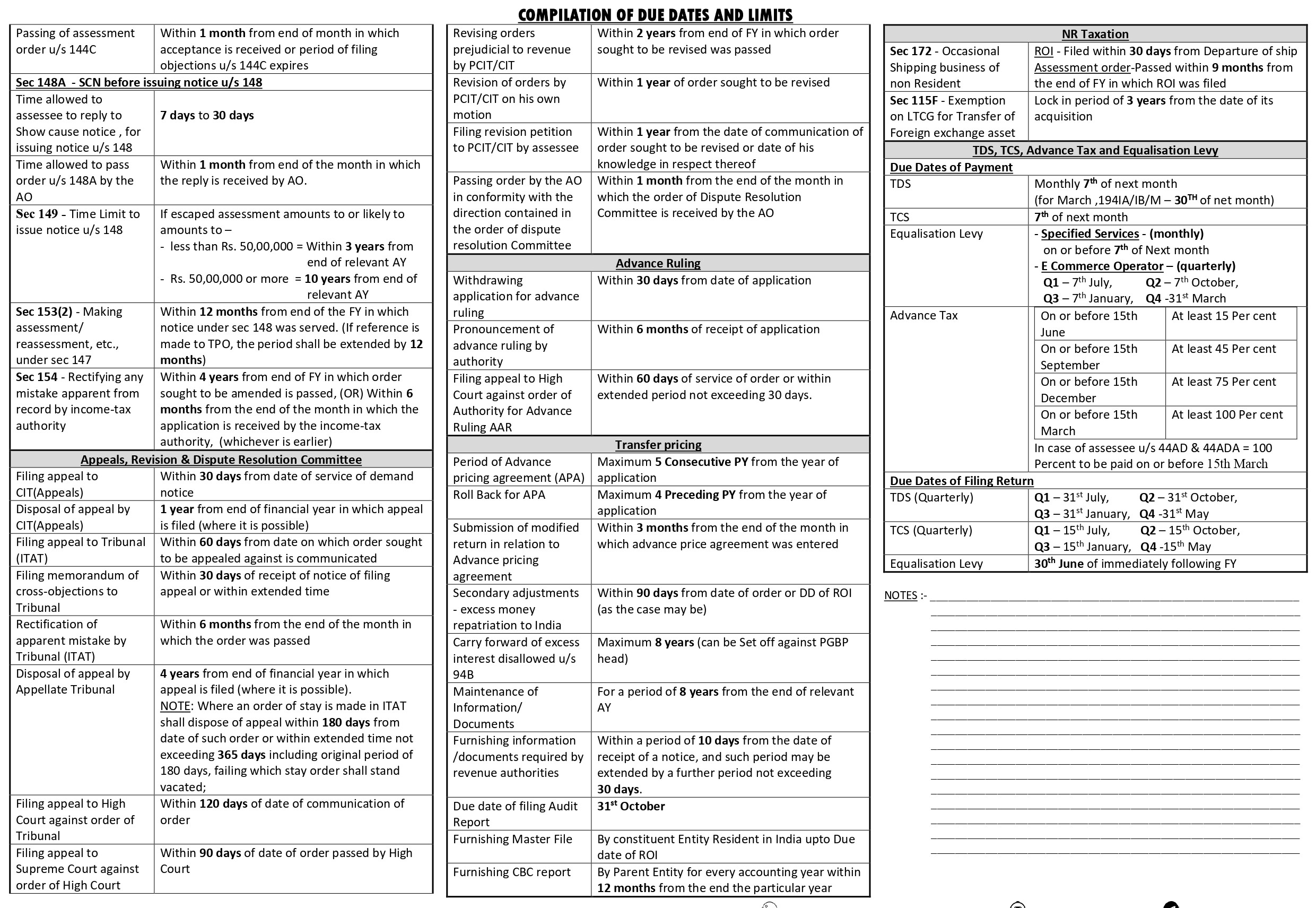
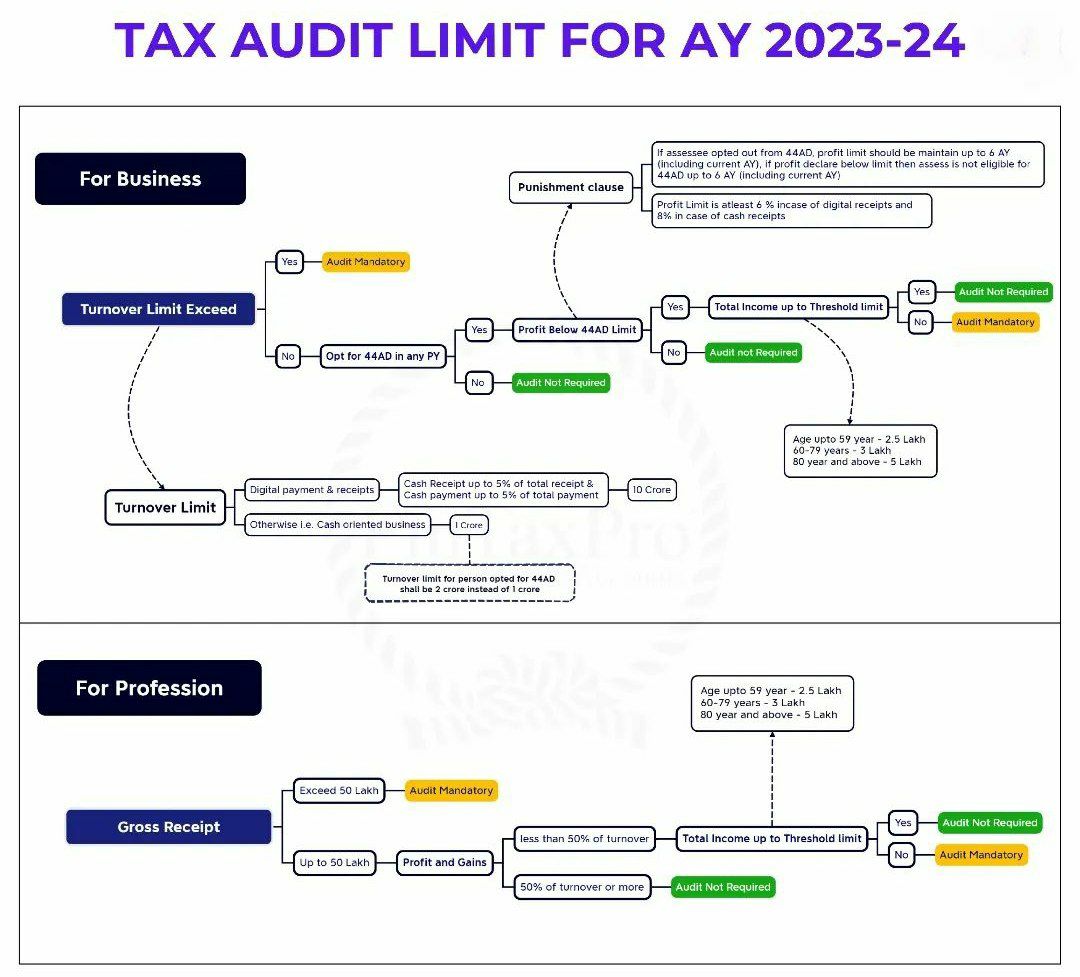
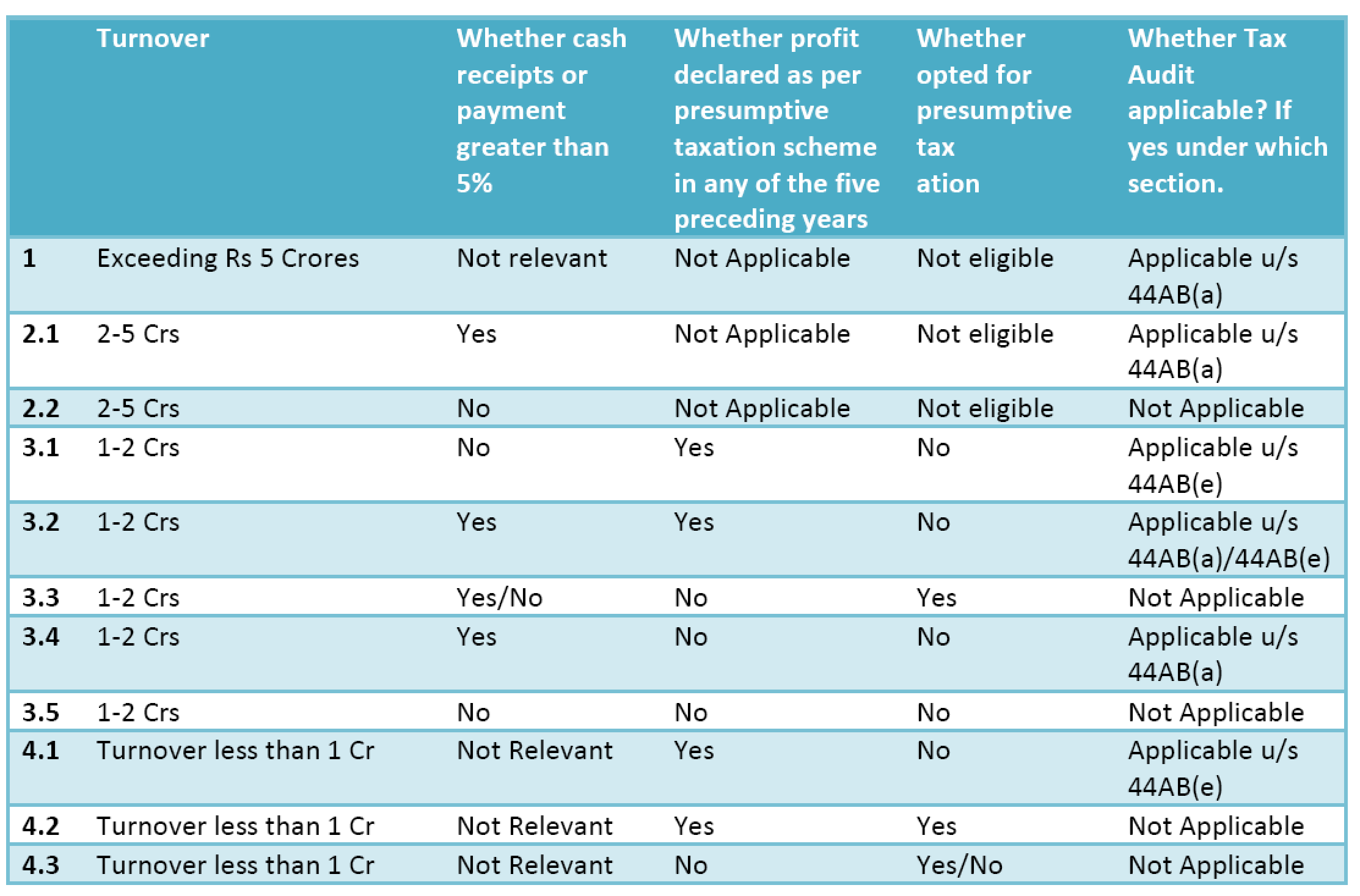
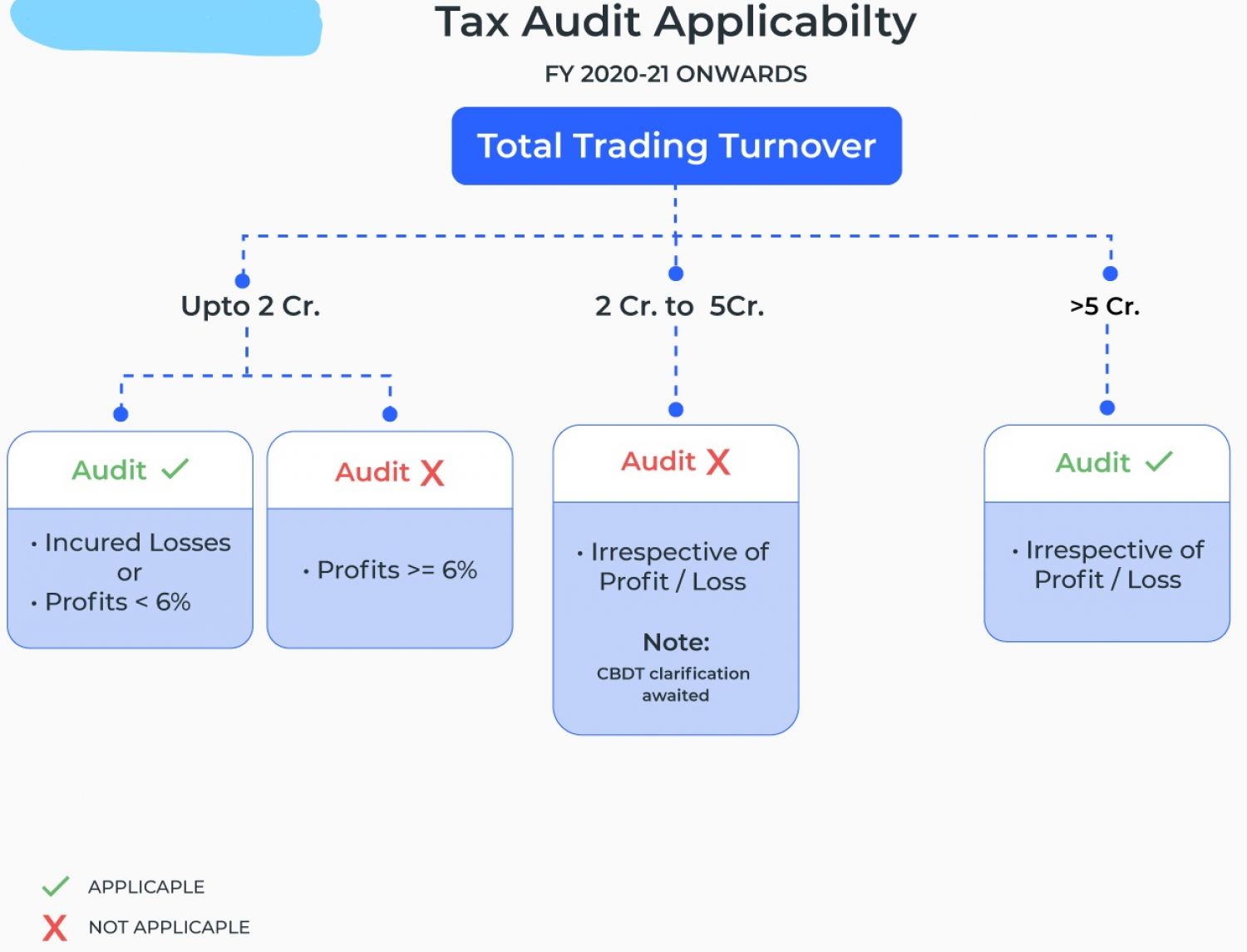
- Applicability of Tax Audit u/s 44AB
- Tax Audit
Popular Articles related to Tax Audit :